
Through this legislation and the support of major U.S., European and Japanese banks, the 1988 Basel Committee on Banking Regulation and Supervisory Practices announced that, for internationally active commercial banks, adequate capital requirements would be raised from 5.5% to 8% of total assets. It was followed by Basel II in 2004, which incorporated types of credit risk in the calculation of ratios. They charge that higher capital requirements have the potential to reduce bank risk-taking and competition in the financial sector (on the basis that regulations always prove costlier to smaller institutions than to larger ones). By mandating banks to keep a certain percentage of assets liquid, the requirements can inhibit the institutions’ ability to invest and make money—and thus extend credit to customers.
- For private companies, a beta is estimated based on the average beta among a group of similar public companies.
- They tend to increase following a financial crisis or economic recession.
- The analysis used Mortgage Portfolio Analyzer (MPA) as the loan-level credit model in the calculation of expected loss (EL) and loss given default (LGD) to assess the credit risk of pools backing the RMBS bonds.
- This analysis looks back at how the sector has evolved over the last four decades and speculate on the near- and long-term effects of COVID-19, as well as the degree of impact by industry and geography.
- The assumption is that a private firm's beta will become the same as the industry average beta.
Analysts must determine the cost of each class, and then create an average that is weighted according to how much of the company’s invested capital comes from each class of capital. The results of our analysis show that the average capital requirements are 14.2% and 21.4% under the SFA and SSFA approaches, respectively, with an average Capital Relief of 7.2% under the SFA method. In the portfolio analyzed, 96% exhibited Capital Relief under the SFA method for an average capital charge of 14.8% and a Capital Relief relative to the SSFA method of 7.5%.
Browse the financial glossary in alpabetical order
While banks are in the process of analyzing which approach to use, this study shows that there are many pool and bond-level characteristics that can assist with the process. (C) The amount of collateral posted by the Bank and held by the derivatives clearing organization, clearing member, or custodian in a manner that is not bankruptcy remote, but only to the extent the amount exceeds the Bank's current credit exposure to the derivatives clearing organization. An angry public and uneasy investment climate usually prove to be the catalysts for legislative reform in capital requirements, especially when irresponsible financial behavior by large institutions is seen as the culprit behind a financial crisis, market crash, or recession. Each category of the firm's capital is weighted proportionately to arrive at a blended rate, and the formula considers every type of debt and equity on the company's balance sheet, including common and preferred stock, bonds, and other forms of debt. Cost of capital, from the perspective of an investor, is an assessment of the return that can be expected from the acquisition of stock shares or any other investment.
The methodology shall involve an evaluation of counterparty or asset risk factors, and may incorporate, but must not rely solely on, credit ratings prepared by credit rating agencies. Each Bank shall align its various internal credit ratings to the appropriate categories of FHFA Credit Ratings included in Table 2 to this section. In doing so, FHFA Categories 7 through 1 shall include assets of progressively higher credit quality. After aligning its internal credit ratings to the appropriate categories of Table 2 to this section, each Bank shall assign each counterparty, asset, item, and contract to the appropriate FHFA Credit Rating category based on the applicable internal credit rating. (iii) The credit risk capital charge for the hedged portion of the non-mortgage asset is equal to the credit risk capital charge for the credit derivative, calculated in accordance with paragraph (e) of this section.
More Definitions of Capital Charges
The Capital Relief is spread across all product types within the 6-10% Capital Relief range. In the case of this portfolio, the product type did not act as a sound indicator of capital relief treatment. (2) Exception for assets subject to a guarantee or secured by collateral. Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance.
A Bank shall use the stress loss percentage for each asset to determine the appropriate FHFA RMA or CMO ratings category for that asset, as set forth in Table 4 to this section. A Bank shall do so by assigning each such asset to the category whose credit risk percentage requirement equals the asset's stress loss percentage, or to the category with the next highest credit risk percentage requirement. For residential mortgages and residential mortgage pools, the methodology shall involve an evaluation of the residential mortgages and residential mortgage pools and any credit enhancements or guarantees, including an assessment of the creditworthiness of the providers of such enhancements or guarantees. In the case of a residential mortgage security or collateralized mortgage obligation, the methodology shall involve an evaluation of the underlying mortgage collateral, the structure of the security, and any credit enhancements or guarantees, including an assessment of the creditworthiness of the providers of such enhancements or guarantees.
TfL ULEZ: Is my car compliant? Do I have to pay a charge? How do I … – LondonWorld
TfL ULEZ: Is my car compliant? Do I have to pay a charge? How do I ….
Posted: Tue, 08 Aug 2023 05:00:00 GMT [source]
Maintaining certain levels of capital can increase their costs, which in turn increases costs for borrowing or other services for consumers. However, as the 21st century advanced, a system of applying a risk weight to different capital charge meaning types of assets allowed banks to hold less capital with total assets. The one weight meant that for every $1 of commercial loans held on a bank's balance sheet, they would be required to maintain eight cents of capital.
Early-stage companies rarely have sizable assets to pledge as collateral for loans, so equity financing becomes the default mode of funding. Less-established companies with limited operating histories will pay a higher cost for capital than older companies with solid track records since lenders and investors will demand a higher risk premium for the former. This article discusses the three approaches for setting capital charges for operational risk as proposed by the New Basel Accord. The article addresses a series of questions raised by the Basel proposal related to defining, measuring, and reserving for operational risk. The author suggests that capital reserves may actually serve as a deterrent to reducing operational losses. As highlighted in this article, the SFA framework could result in significant regulatory capital relief when compared to the SSFA framework.
Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC)
The least amount of money that banks and depository institutions are required to maintain is referred to as capital requirement. This amount should never be claimed, should never be lent and should not be on debt. This amount is set by Federal Reserve Bank, Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, State Banking Regulators and Bank for International Settlements. Capital requirements are set to ensure bank and depository institution holdings are not dominated by investments that increase the risk of default. They also ensure that banks and depository institutions have enough capital to sustain operating losses (OL) while still honoring withdrawals.
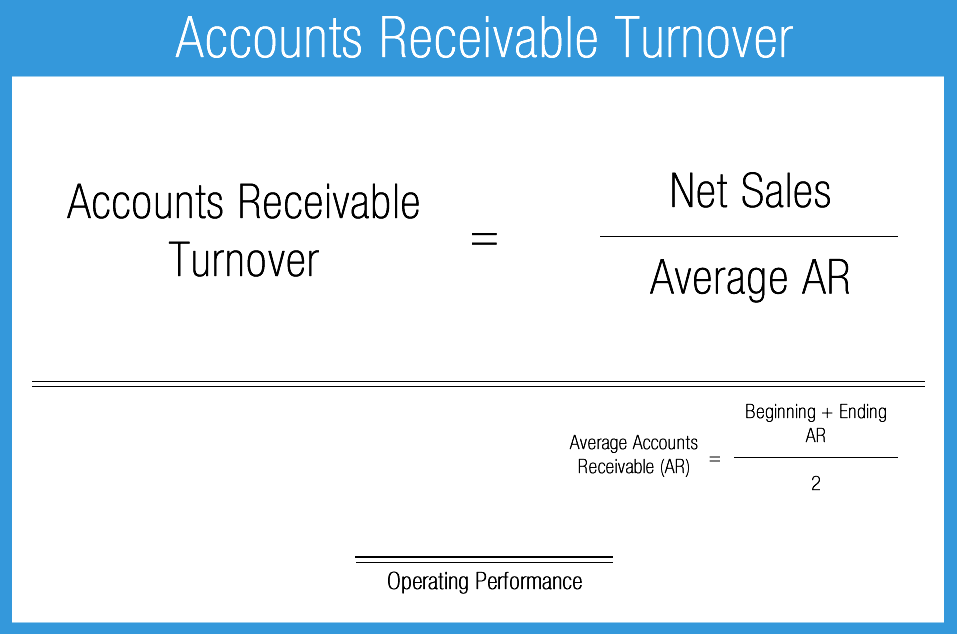
(i) Each Bank's credit risk capital charge for a residential mortgage, residential mortgage pool, residential mortgage security, or collateralized mortgage obligation shall be equal to the asset's amortized cost multiplied by the credit risk percentage requirement assigned to that asset pursuant to paragraph (g)(1)(ii) or (g)(2) of this section. For any such asset carried at fair value where any change in fair value is recognized in the Bank's income, the Bank shall calculate the capital charge based on the fair value of the asset rather than its amortized cost. Each Bank's credit risk capital requirement shall equal the sum of the Bank's individual credit risk capital charges for all advances, residential mortgage assets, CMOs, non-mortgage assets, non-rated assets, off-balance sheet items, and derivative contracts, as calculated in accordance with this section. (b) Credit risk capital charge for residential mortgage assets and collateralized mortgage obligations.
The Basics of Capital Requirements
The cost of capital is also high among both biotech and pharmaceutical drug companies, steel manufacturers, internet software companies, and integrated oil and gas companies. Those industries tend to require significant capital investment in research, development, equipment, and factories. Since a company with a high cost of capital can expect lower proceeds in the long run, investors are likely to see less value in owning a share of that company's equity.
On the REIT Track Morrison & Foerster LLP – JDSupra – JD Supra
On the REIT Track Morrison & Foerster LLP – JDSupra.
Posted: Fri, 04 Aug 2023 17:39:35 GMT [source]
Homebuilding has a relatively high cost of capital, at 6.35, according to a compilation from New York University's Stern School of Business. Cost of capital is a company's calculation of the minimum return that would be necessary in order to justify undertaking a capital budgeting project, such as building a new factory. How will COVID-19 reshape the dynamics of office space as an income-generating asset class? This analysis looks back at how the sector has evolved over the last four decades and speculate on the near- and long-term effects of COVID-19, as well as the degree of impact by industry and geography. While the SFA-based regulatory Capital Relief spans across the granularity scale, we observe the EL and LGD for the underlying exposure as expected.
Regulatory capital relief
In the analysis, observed securities floored at the regulatory capital floor for both approaches. Furthermore, it is conceivable that for some securities backed by poor quality and concentrated pools, a higher capital charge is present under the SFA as compared to the SSFA. Nonetheless, in most cases the SFA method was found to provide fairly significant Capital Relief relative to the more prescriptive SSFA method. For this analysis, a large RMBS portfolio was considered, along with loan-level credit analytics to estimate pool losses of underlying residential mortgages. The analysis used Mortgage Portfolio Analyzer (MPA) as the loan-level credit model in the calculation of expected loss (EL) and loss given default (LGD) to assess the credit risk of pools backing the RMBS bonds. Figure 6 helps highlight the Capital Relief levels of the tranches that are currently rated below investment grade (Ba and lower).
- However, as the 21st century advanced, a system of applying a risk weight to different types of assets allowed banks to hold less capital with total assets.
- In the case of a residential mortgage security or collateralized mortgage obligation, the methodology shall involve an evaluation of the underlying mortgage collateral, the structure of the security, and any credit enhancements or guarantees, including an assessment of the creditworthiness of the providers of such enhancements or guarantees.
- Each type of capital has a different cost because investors treat each class of investments differently.
- The credit risk capital charge for a non-mortgage asset that is hedged with a credit derivative that has a remaining maturity of one year or more may be reduced only in accordance with paragraph (j)(3) or (4) of this section and only if the credit derivative provides substantial protection against credit losses.
- A Bank shall use the stress loss percentage for each asset to determine the appropriate FHFA RMA or CMO ratings category for that asset, as set forth in Table 4 to this section.
- An investor might look at the volatility (beta) of a company's financial results to determine whether a stock's cost is justified by its potential return.
For this analysis, the approach in this section was deemed to be the most appropriate. Even though original ratings did not prove to be diverse enough to properly indicate levels of Capital Relief, due to the fact that most trusts within the given vintage range have their mezzanine and junior tranches written off, the current Moody’s rating was a better indicator of Capital Relief levels. When analyzing the portfolio by current pool factor, Capital Relief is present across the range except at the tail-end due to low delinquencies and defaults at the top-end, and very low tranche thickness at the bottom-end.
The company can also sell bonds, which create loans from investors to the company, and this type of capital is debt capital. The total amount of invested capital can be found by taking the company’s capital listed on its balance sheet and adjusting it so it also shows the capital not reported there. As highlighted in this article, the SFA framework could result in significant regulatory Capital Relief when compared to the SSFA framework.
(E) Subject to an appropriate discount to protect against price decline during the holding period and the costs likely to be incurred in the liquidation of the collateral.
